One of the most renowned military organizations in the world is the Indian Navy. For many young hopefuls, joining the Indian Navy is a dream come true. The protection of the nation’s marine borders is the duty of the Indian Navy. Candidates who are keen on joining should be aware of the ranks in Indian Navy. A candidate should be well informed about the ranks in Indian Navy as one should know everything about what they want to be. So, this article is the one-stop solution for every individual who wants to join the Indian Navy and wants to know about the ranks in Indian Navy.
Read More – Indian Navy Agniveer Preparation Tips
Ranks In Indian Navy and Insignia
The three broad types of Indian Navy Ranks are Officer Ranks, Junior Commissioned Officers, and Other Ranks.
In most cases, these ranks match those of the British military ranks. There are still certain ranks with traditional names.
All the ranks in Indian Navy are enlisted in the tables below in descending order of control.
Indian Navy Ranks ( Commissioned Officer )
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Admiral of the fleet (Honorary/ Wartime rank) |  |
| Admiral (The Chief of the Naval Staff) |   |
| Vice Admiral |   |
| Rear Admiral |   |
| Commodore |  |
| Captain |  |
| Commander |  |
| Lieutenant commander |  |
| Lieutenant |  |
| Sub-lieutenant |  |
| Midshipman | 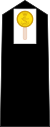 |
Ranks In Indian Navy ( Junior Commissioned Officer )
| Ranks | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Master chief petty officer 1st class |  |
| Master chief petty officer 2nd class |  |
| Chief petty officer |  |
Indian Navy Ranks ( Non-Commissioned Officer )
| Ranks | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Petty officer |  |
| Leading seaman |  |
| Ordinary seaman | No insignia |
Indian Navy Rank List – Explained
Commissioned Officer Ranks –
Admiral of the fleet – A fleet admiral, sometimes known as an admiral of the fleet, is a senior naval flag officer position that is often equivalent to a Field marshal and an air force Marshal. Typically, an admiral of the fleet is superior to an admiral.
A senior admiral in charge of a sizable collection of ships, such as a fleet or, in some situations, a group of fleets, is also referred to by this general phrase.
Admiral – In the Indian Navy, the rank of admiral is a four-star naval flag officer. The Indian Navy’s highest active rank is this one. Vice admiral is a three-star position below admiral, and admiral of the fleet is a five-star title that has never been granted or held.
To differentiate an admiral from lower flag officer levels like vice admiral and rear admiral, they may be referred to as a full admiral or four-star admiral.
Since 1968, the professional commander of the Indian Navy, the Chief of the Naval Staff (CNS), has held the position. If the holder is a flag officer currently serving in the Indian Navy, the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) may also hold the position.
Vice Admiral – A three-star flag officer rank in the Indian Navy is Vice admiral. The Indian Navy’s second-highest active rank is this one. The two-star rank of rear admiral and the four-star rank of admiral, which is held by the Chief of the Naval Staff (CNS), are below vice admiral, respectively.
In the Indian Army, a lieutenant general is the comparable rank, and in the Indian Air Force, an air marshal.
Vice admiral officers have significant positions in the naval commands and at the military headquarters.
Rear Admiral – The Indian Navy’s two-star flag officer rank of rear admiral. In the Indian Navy, it is the third-highest active rank. The rank of Rear admiral is below the three-star level of vice admiral and above the one-star rank of commodore.
Major General and Air Vice Marshal, respectively, are the comparable ranks of the Indian Armed Forces.
Commodore – In the Indian Navy, the rank of commodore is one star. Rear admiral, a two-star rank, is placed behind commodore and captain, respectively.
In the Indian Army, the corresponding rank is brigadier, while in the Indian Air Force, it is air commodore.
Captain – The Indian Navy has a rank called captain. A Captain is ranked beneath a Commodore and above a Commander. It is comparable to group captain in the Indian Air Force and colonel in the Indian Army.
Commander – Both a rank for naval officers and a job title in various armies, commander. The term or rank of “commander” is frequently used in other official organisations, such as several police forces. This naval rank is known as a frigate captain in a number of countries.
Commander is ranked below Captain and above Lieutenant commander in Indian Navy.
Lieutenant Commander – Many navies, including the Indian Navy, have a commissioned officer rank known as lieutenant commander. The rank is beneath a commander and above a lieutenant. Major is the equivalent rank in the majority of armies and air forces.
On many warships and smaller shore facilities, a lieutenant commander is a department officer, the executive officer (second-in-command), or the commanding officer of a smaller ship or post.
Lieutenant – Lieutenant is a commissioned officer rank in Indian Navy. It is typically the most senior of junior officer ranks. It ranks below the lieutenant commander and above the Sub-lieutenant.
Sub-lieutenant – A sub-lieutenant is usually a junior officer rank, used in armies, navies, and air forces of India.
In Indian Navy, the sub-lieutenant is ranked below lieutenant and above midshipman.
Midshipman – The lowest ranking officer in the Royal Navy, US Navy, and several Commonwealth navies is called a midshipman. The National Defence Academy or the Indian Naval Academy is where midshipmen in the Indian Navy begin their training as cadets, where they spend about three years. After graduating, they are given training ships to work on for a year before receiving a BTech degree from Jawaharlal Nehru University. The cadets are promoted to midshipman status after six months on the training ship. Midshipmen are evaluated by a board at the conclusion of their training in order to be approved for advancement to sub-lieutenant.
Junior Commissioned officer Ranks –
Master chief petty officer -Master chief petty officer is a junior commissioned officer rank. In the Indian Navy, there is an enlisted rank known as master chief petty officer (MCPO). The promotion to master chief petty officer in the Navy is the same as the promotion to chief petty officer and senior chief petty officer. It has criteria for length of service, excellence in evaluations, and selection by a master chiefs’ board. Chief petty officers and senior chief petty officers are also chosen by selection committees.
Chief Petty Officer – A Chief Petty Officer is a junior-commissioned officer in the Indian Navy who is equivalent to the NATO rank of E-6 (Staff Sergeant). This rank is equivalent to Junior Warrant Officer in the Indian Air Force and Naib Subedar in the Indian Army.
Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks –
Petty Officer – In the Indian Navy, a petty officer is a non-commissioned officer who has the OR-6 enlisted grade in NATO. They hold the same rank as a sergeant in the Indian Army and Indian Air Force, or a sub inspector of police in the Indian Police Services. As is the situation in the majority of Commonwealth fleets, a petty officer is above in rank to a leading rate and below a chief petty officer.
A petty officer has the leadership skills necessary to manage a team of employees and participate in the recruitment and training of new Indian Navy recruits.
Leading Seaman – A junior non-commissioned rank or rate in navies, notably those of the Commonwealth, is called a leading seaman. Leading Seaman’s rank code, when used by NATO countries, is OR-4. Some navies use corporal instead of leading seaman because it is frequently equivalent to the rank of corporal in the army and the air force.
Ordinary Seaman – The deck department of a ship is made up of ordinary seamen (OS). It has been an apprenticeship to become a skilled seaman for ages. The term “sea time” refers to the length of time an OS must spend working aboard a ship in the modern era. For centuries, a seaman with one to two years of sea time who demonstrated sufficient seamanship to be rated as such by their captain was referred to as an “ordinary seaman.” Historically, a sailor with less experience was referred to as a landsman in several navies and the merchant marine.
How long does it take to become Admiral in Indian Navy –
How long it takes to rise to the rank of Admiral in the Indian Navy is not known with any precision. The term of the Indian Navy Chief, who holds the rank of Admiral, is understood to be either three years or until the age of 62, whichever comes first. Through promotions, training, and the acknowledgment of effort, sincerity, skills, and talent, the Indian Navy provides practically endless opportunities for aspiring sailors and commanders to create a career and climb the professional ladder.
Indian Navy Pay Scale (Officer)
| RANK | PAY SCALE (in Rs.) |
|---|---|
| SUB LIEUTENANT | 56100-177500 |
| LIEUTENANT | 61300-193900 |
| LIEUTENANT COMMANDER | 69400-207200 |
| COMMANDER | 121200-212400 |
| CAPTAIN | 130600-215900 |
| COMMODORE | 139600-217600 |
| REAR ADMIRAL | 144200-218200 |
| VICE ADMIRAL | 182200-224100 |
| VICE ADMIRAL AND EQUIVALENT | 205400-224400 |
| DGAFMS | 225000 |
| VCNS / C-IN-C/ EQUIVALENT | 225000 |
| CNS / EQUIVALENT | 250000 |
Indian Navy Pay Scale ( Other Ranks)
| Rank | Pay Band in Rs. | Grade pay |
|---|---|---|
| Seaman II | 5200-20200 | 2000 |
| Seaman | 5200-20200 | 2400 |
| Leading Seaman | 5200-20200 | 2800 |
| Petty Officer | 5200-20200 | 2800 |
| Chief Petty Officer | 9300-34800 | 4200 |
| MCPO II | 9300-34800 | 4600 |
| MCPO I | 9300-34800 | 4800 |
Conclusion
Candidates interested to join the Indian Navy should know about the Indian Navy ranks, hierarchy, and salary structure which are mentioned in the article aforementioned.
Joining the Indian Navy and serving the nation is a matter of pride for every individual. So if you are looking for a career option in the Indian Navy then the rank structure is something you should be aware of.
Look forward to our upcoming articles for more exposure regarding the defense sector of the country!
Read More – Indian Army Ranks and its Insignia
